What is Habit Disruption?
Habit Disruption is a concept in behavioral science that pertains to the interruption or breaking of a habit. It refers to a process or an event that changes the cues or routine associated with a habit, or otherwise interferes with its performance.
Definition
Habit Disruption refers to the process of breaking a habit, either by changing the environmental cues associated with the habit, altering the habitual behavior itself, or changing the outcomes or rewards that follow the behavior. Habit disruption can occur naturally due to changes in one’s life or environment, or it can be a deliberate process undertaken to change unwanted behaviors.
Key Aspects
-
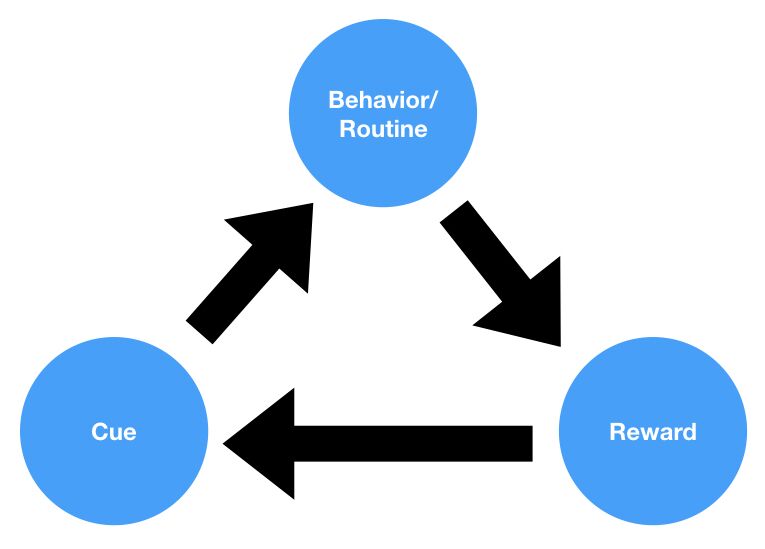
Change in Cues
Habit disruption often involves a change in the cues that trigger the habit. This might be a change in one’s environment, daily routine, or the people one interacts with.
-
Alteration of Routine
Another aspect of habit disruption is the alteration of the habitual behavior or routine. This could involve replacing the old behavior with a new one, or making changes to the way the behavior is performed.
-
Change in Outcome
Habit disruption can also involve a change in the outcome or reward associated with the habit. If the reward no longer follows the behavior, or if the outcome is negative rather than positive, the habit may be disrupted.
Role in Behavioral Science
In behavioral science, habit disruption is a valuable concept for understanding how habits can be changed or broken. It also helps us understand why major life changes or shifts in environment can often lead to changes in behavior. Understanding habit disruption is key to creating effective interventions for behavior change.
Implications for Behavior Change
Habit disruption is a crucial tool for behavior change, particularly for changing undesirable habits. By disrupting the habit loop — the cue, routine, reward cycle — one can break old habits and pave the way for new, more beneficial ones. Strategies for habit disruption can include changing one’s environment to remove cues, finding new behaviors to replace the old ones, or changing the outcomes associated with the habit.